Sustainability Strategy
Having a clear, well-defined sustainability strategy is essential for addressing today’s complex business challenges, from reputational risk to inclusion and equity considerations to climate-related concerns. As stakeholder expectations and regulatory demands continue to grow, so does the need for timely, focused action. Weaver helps organizations build a practical, actionable roadmap that begins with a materiality assessment to prioritize what matters most and drive meaningful results.
Connect with usTrending
Insights & Resources
Approach sustainability with clarity and purpose.
A thoughtful, measurable sustainability strategy requires more than good intentions — it takes structure, insight and an informed approach that aligns with your business priorities. Weaver leverages years of experience to help organizations prioritize key sustainability issues, align with global standards and achieve results.
Materiality and Double Materiality Assessment
An effective sustainability strategy starts with understanding issues that matter most to both your organization and stakeholders. A materiality assessment serves as a critical tool in this process, guiding your organization to:
- Identify and prioritize sustainability topics
- Evaluate topic importance to internal and external stakeholders
- Assess the topics’ potential impact — both risks and opportunities — on business operations
By systematically engaging internal and external stakeholders, including employees, investors, suppliers, communities and advocacy groups, materiality assessments ensure a comprehensive view of sustainability priorities and a clear pathway to informed decision-making.
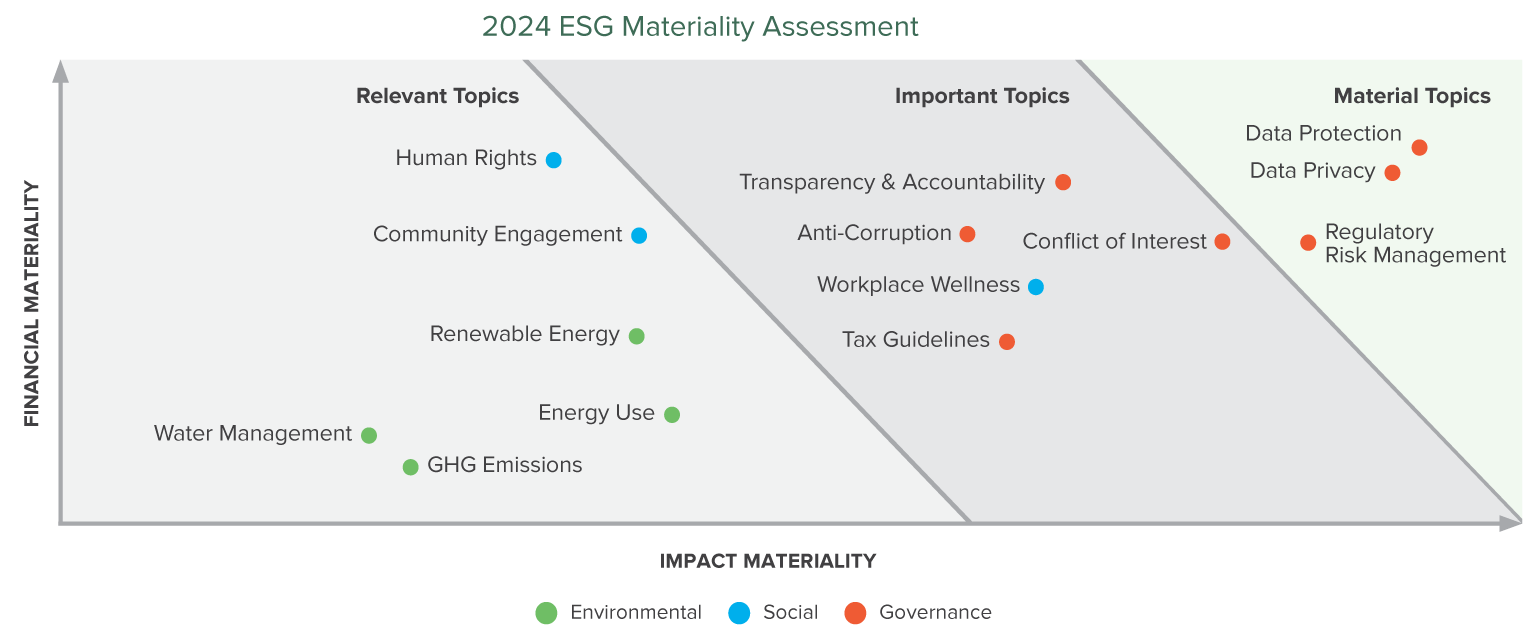
Taking this a step further, a double materiality assessment expands upon traditional materiality by assessing both the financial impacts of sustainability issues on your organization and the external impacts your organization has on society and the environment.
Recognized as the new gold standard within the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), double materiality requires a deeper analysis of sustainability impacts, risks and opportunities. This rigorous assessment validates and substantiates the identified sustainability topics, positioning your organization to:
- Proactively address stakeholder concerns
- Align strategic initiatives with global frameworks and reporting standards
- Demonstrate leadership in responsible business practices
Adopting double materiality not only improves risk management but also creates strategic opportunities to enhance corporate reputation, attract talent and exceed investor expectations.

Sustainability Development
Building a robust sustainability development plan involves aligning organizational sustainability goals with overall business objectives, creating a direct pathway to measurable impact. A well-structured plan identifies priorities through materiality assessments and sets achievable and science-based targets with defined actionable plans to reach these targets. The plan guides the program roadmap, translating complex sustainability concepts into practical initiatives and embeds sustainability into everyday business decisions and operations.
A comprehensive sustainability development plan should deliver business-aligned results that effectively reduce risk, increase value and protect your brand reputation among both customers and employees. This approach must draw on executive leadership’s input, reflecting the company’s long-term vision and aligning closely with organizational core values. It is also essential to consider internal bureaucracy and change management dynamics to ensure successful implementation.
Together, we’ll collaborate with you to develop a customized sustainability plan that’s built for meaningful and long-term success, enabling your organization to:
- Foster long-term resilience
- Strengthen stakeholder relationships
- Solidify its committed position to responsible growth
Sustainability Program Roadmap
Once a clear sustainability strategy that’s informed by materiality assessments is in place, the next step is to define how that strategy will come to life. The sustainability program roadmap outlines specific initiatives, policies and actions needed to achieve your sustainability objectives.
Distinct from the strategy, which focuses on broad, long-term goals, the roadmap provides a practical, phased approach to implementation. It details immediate, intermediate and future-focused actions tailored to your organization’s needs.
The roadmap also:
- Identifies key priorities
- Assigns responsibilities across teams
- Establishes a framework to monitor and track progress
With this structured plan, leadership and teams are able to confidently navigate internal processes, manage resources efficiently and drive sustainability objectives forward. The roadmap transforms strategic intent into tangible actions, enabling sustained progress and meaningful impact across environmental, social and governance areas.
Gap Analysis
After defining the sustainability program roadmap, the next step is to assess your organization’s current state and readiness to execute the roadmap as planned. A gap analysis evaluates existing operations, personnel, internal processes, reporting structures and technology systems against the expectations outlined in the roadmap.
This evaluation helps establish a clear baseline and determine whether the necessary resources and capabilities are in place to support implementation.
Common gap areas that may arise include:
- Staffing and internal ownership
- Systems and data availability
- Institutional processes and decision-making readiness
Because sustainability spans a broad set of functions, a gap analysis ensures that implementation is both feasible and effective, minimizing wasted effort and aligning progress with core business goals. This critical checkpoint also informs timing, sequencing and support needs, supporting you to operationalize your initiatives successfully.
Decarbonization Roadmap
While it’s part of your broader sustainability strategy, the decarbonization roadmap is treated as a distinct workstream due to the technical complexity, data requirements and financial impact it involves. The decarbonization roadmap often represents the most financially impactful component of the sustainability program, uncovering opportunities to reduce energy use — directly lowering operating expenses — and is a catalyst for climate-driven innovation.
The process to create this roadmap begins by:
- Defining the organizational boundary, including establishing which entities, assets and activities are included in emissions accounting
- Mapping current emissions across scopes and facilities
- Evaluating infrastructure, procurement strategies and resource use to identify reduction opportunities
Based on this analysis, the roadmap identifies appropriate pathways for decarbonization, which may include:
- Electrification of operations
- Renewable energy sourcing
- Energy efficiency upgrades
- Supply chain engagement, prioritized based on feasibility, cost and business impact
The roadmap also considers the organization’s operational realities, budget cycles and change readiness to ensure implementation is realistic and actionable.
To strengthen credibility and comparability, the decarbonization roadmap is aligned with the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi), which provides a standardized, science-backed framework for setting and validating emissions reduction targets. This alignment ensures consistency in tracking progress and enhances transparency in climate reporting.
More than a technical exercise, the decarbonization roadmap helps translate sustainability commitments into measurable results. It enables organizations to:
- Sequence initiatives thoughtfully
- Align internal teams around shared goals
- Invest strategically for long-term climate and business performance